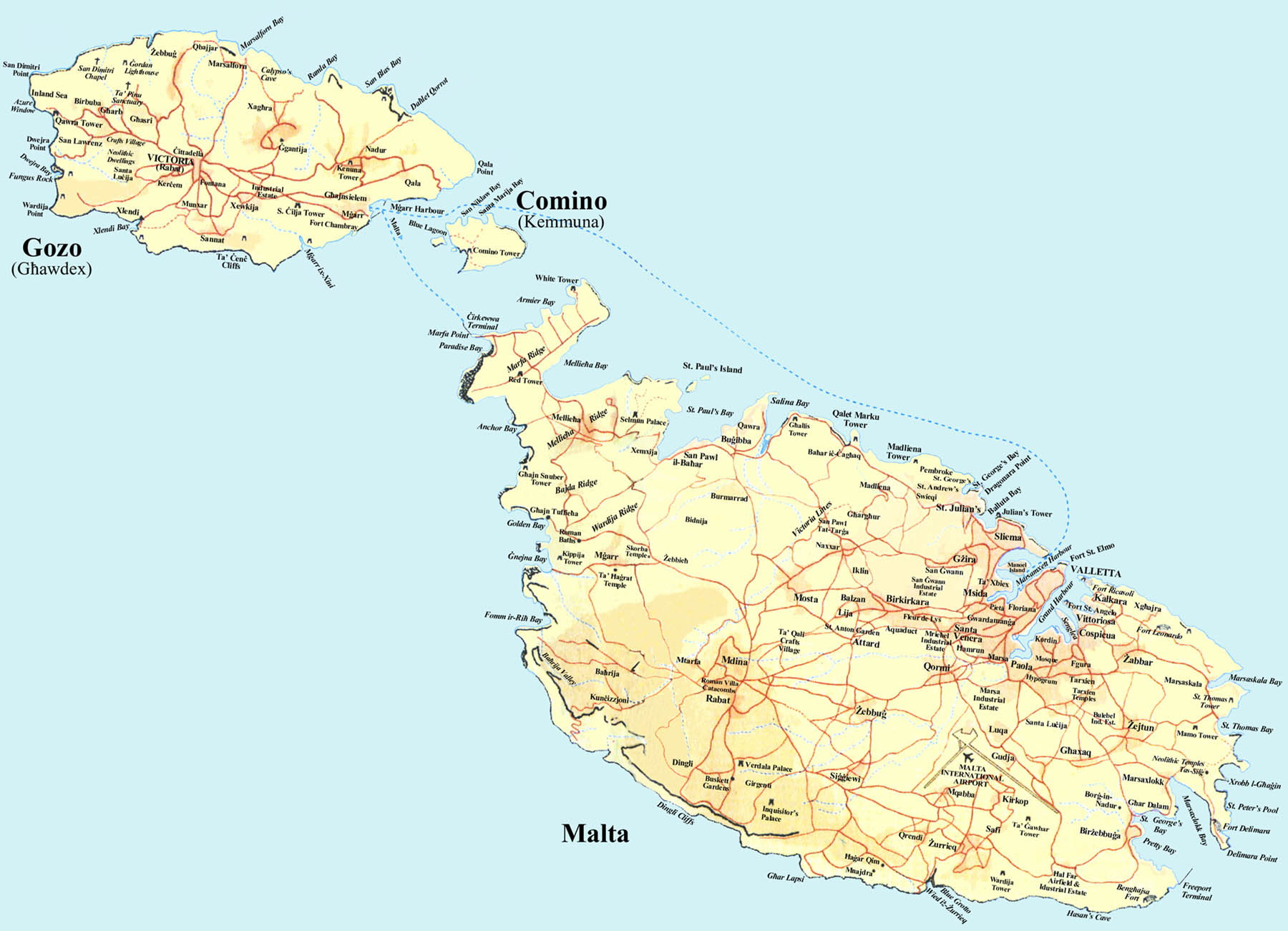
GEOGRAPHIC LOCATION
The Maltese archipelago is strategically positioned in the middle of the Mediterranean, the centre point of Europe and Africa with the largest inhabited island, Malta, lying 93km (180miles) from North Africa. Gozo and Comino are the only other inhabited Islands. Known as the Jewel of the Mediterranean the landscape of all three is characterised by low hills with terraced fields.
Malta has no mountains or rivers. Its coastline is indented with harbours, bays, creeks, sandy beaches and rocky coves. Complimented with deep blue waters, Gozo is connected to Malta by ferry and is more thickly vegetated, with many flat-topped hills and craggy cliffs. Comino, the smallest Island, is connected to Malta and Gozo by ferry and is very sparsely populated.
The Maltese Islands enjoy a healthy Mediterranean climate that of year round sunshine with mild winters and hot summer seasons nicknamed the ‘Island of Vitamin D’. Cold winds, snow, frost and fog are unknown. Rain falls between September and April. It seldom rains after April, and nearly never in summer time. The temperature averages 57.5 degrees Fahrenheit in winter (Nov-Apr) and 89.6 degrees Fahrenheit during the summer (May-Oct). The hottest period is from mid-July through mid-September although the islands seldom get too hot, as hot summer days and nights are regularly tempered by cool sea breezes.
The majority of fields are small and terraced, but despite lack of rain and other adverse terrain conditions, agriculture is well developed.
BRIEF HISTORY
For 7000 years the Islands attracted visitors with different cultures, who influenced the Islands’ heritage.
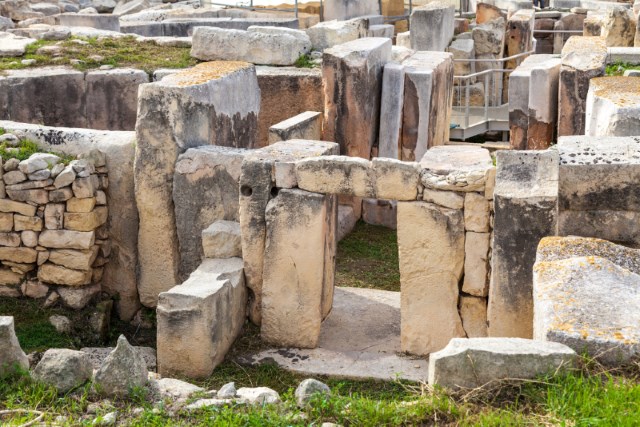

The first Maltese were Stone Age farmers who came from Sicily about 4,000 B.C. They maintained trade links with their original homeland. Later they built magnificent stone temples dedicated to a Mother Goddess of Fertility.
About 2,000 B.C. Bronze-Age warriors from Southern Italy came and supplanted the farmer population. These warriors left walled settlements and the cart-ruts spread all over the Island.
By 800 B.C. Phoenician merchants had colonized the island. These settlers were peaceful and clever traders and are known as Punic in origin. The Maltese probably are the descendants of much Punic stock.
These peaceful settlers were conquered by the Romans about 218 B.C. and Malta came to form part of the Roman Empire. The Maltese eventually became Roman citizens with a measure of autonomy.
The Island became Christian in 60 A.D. when St. Paul was shipwrecked on the island. Remains from this period, mostly around the Rabat and Mdina area, testify to a cultured class of Maltese citizens.
The Arabs took over as conquerors in 870 A.D. and Christianity petered out until it surfaced again with the coming of the Normans in 1090 and 1127. Malta came to form part of the province of Sicily and underwent the same changes as its bigger island neighbour seeing a chain of new conquerors such as the Swabians, Angevins, Aragonese and Castillians until the year 1530 when the order of the Knights of St. John were given the Islands of Malta and Gozo by the German Empire Charles V.
The Knights turned Malta into a small nation and built palaces, churches and defences which are still in existence today. The victory over the Turks in 1565 marked a new beginning for Malta as a European and Christian Island.
The state of affairs came to an end with the conquest of the island by Napoleon in 1798 and the consequent ousting of the French by the British in 1814. Malta became a part of the great British Empire until it became a totally independent and sovereign state in 1964, followed by becoming a Republic in 1974. Today it forms part of the European Union having joined on 1 May 2004.
THE CAPITAL: VALLETTA
A UNESCO unique heritage city built by the gentlemen for the gentlemen located in South East of Malta this city was built on a hill called Mount Sceberras by the Knights of Malta in the 16th century. This city is one of the richest in heritage of baroque architecture and unique buildings. In addition, the large natural Grand Harbour makes the city one of a kind. Besides a great number of shops, one can find the parliament, law courts and government departments located here.
Valletta is officially the European Culture City in 2018.
AREA
316 sq km (122 sq miles)
POPULATION DENSITY
1189.0 per sq km. Spread in towns and villages especially in the south.
MALTESE AND GOZITANS CULTURE
The Maltese are friendly, very warm, amicable, helpful, courteous and tolerant. The Maltese love visitors and make sure that they make you feel at home.
RELIGION
The islands are predominantly Roman Catholic. However one can find churches of other denominations and a mosque and other religion are practised freely.
LANGUAGE
Maltese (a Semitic language), English and Italian are widely spoken.
CURRENCY
Euro
MEDICAL HEALTH
Government maintains a large, state-of-the-art hospital called Mater Dei Hospital. The National Health Service is free of charge and there are health agreements with many countries. Private hospitals and private health care also exists on Malta.
CLIMATE
Malta’s climate is typical of the Mediterranean and is strongly influenced by the sea. The Maltese Islands have a pleasantly sunny climate with a daily average of around 12 hours sunshine in summer going down to 5 to 6 hours in mid-winter.
Summers are hot, dry and very sunny. Day-time temperatures in summer are often mitigated by cooling sea breezes.
Spring and autumn are cooler, except when the occasional Scirocco wind from Africa brings unseasonally high temperatures and humidity.
Winters are mild, with the occasional short cold spells brought about by the north and north-easterly winds from central Europe.
Annual rainfall is low, averaging 568mm a year. Bathing in the sea is quite possible well into the ‘winter’ months, and the peak beach season can last until mid- to late October.
WATER
Tap water is safe to drink throughout the Maltese Islands. Local and imported bottled mineral water is available from shops, supermarkets, restaurants and bars.
SPORTS
The most popular are football, yachting, water polo, basketball, golf and scuba diving.
ECONOMY
Tourism, ICT, Financial Services, iGaming, Real Estate, English Language Schools and recently named the Blockchain Island.
GOVERNMENT
The Maltese Islands are a Republic and gained independence from the UK in 1964. The head of state is the president. The head of the government is the prime minister. Malta joined the European Union in 1st May 2004.
TIME
GMT + 1
ELECTRICITY
240 volts AC, 50Hz. UK style 3-pin plug are in use.
COMMUNICATIONS
Telephone: IDD is available. Country Code: +356. Outgoing International Codes: 00. Public telephone booths are widely available. Mobile telephone: dual band network with extensive coverage of land and sea.
FERRY SERVICE
The Gozo channel company operates an all year round ferry service between Cirkewwa, Malta and Mgarr, Gozo. Journey time is approximately 20 minutes.
GETTING HERE TO MALTA
By air: Malta International Airport in Luqa services Air Malta / Lufthansa / Alitalia / British Airways / Ryanair / Easy Jet/ Turkish Airlines / Wizz Air / Emirates / Ethihad / Qatar airways. Flights operate daily to Europe, Far East, North America and North Africa. Malta is also served by cruise liners and catamarans from the Grand Harbour of Valletta.
TRANSPORT
Public transport, by bus service are at very low rate and there are taxi services.
No trains or underground trains are found on the Island.
DRIVING
Maltese drivers drive on the left. The extra urban speed limit is 60 km/h and in towns it is 35 km/h.
EDUCATION
State schools are free. The University of Malta runs a wide range of degree courses. There is also a selection of private schools.
